How to produce Calippo style ice cream?
Want to produce Calippo-style ice cream but find the process confusing? Scaling up production from a small test kitchen to a full-scale factory can be a huge challenge. I will guide you through the essential steps for successful, high-volume production.
To produce Calippo-style ice cream, you first create a high-quality ice cream base using a pasteurization and homogenization system. Then, you freeze this mix into a soft consistency. Finally, you use a specialized cup filling and sealing machine to inject the ice cream into paper tubes and seal them.

That’s the basic overview, but as I’ve learned from my years in this business, the success is always in the details. A simplified view can lead to costly mistakes. I remember a new client from Morocco who was struggling with inconsistent freezing temperatures, which caused his entire production line to jam. Getting each stage right is critical for quality and efficiency. Let’s dive deeper into what each stage really involves, from crafting the perfect ice lolly mix to the final automated packaging. Understanding these details will help you avoid common pitfalls and truly accelerate your food production.
How to make a Calippo ice lolly mix?
Is your ice lolly mix not quite right, resulting in a coarse, icy texture? Inconsistent quality can quickly ruin your brand’s reputation and lead to customer complaints. I will show you how to prepare the perfect, smooth base for your Calippo-style treats.
To make the Calippo ice lolly base, you must precisely blend ingredients like milk solids, fats, sugars, and stabilizers. Then, you use an industrial system to pasteurize for safety, homogenize for a smooth texture, and finally age the mix to perfect its structure before freezing. This preparation is critical.
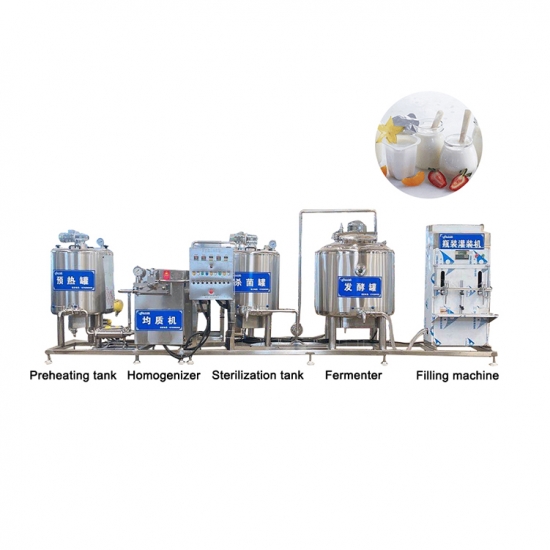

Creating the perfect ice lolly mix is far more than just stirring ingredients together; it’s a precise science that forms the foundation of your final product. I’ve seen many companies, especially in markets like India and Pakistan where dairy quality is a point of pride, invest heavily in getting this stage right. The quality and function of each ingredient directly impact the final taste, texture, and stability of the ice cream. Let’s break down the components and the process.
The Science Behind the Ingredients
Every ingredient has a specific job to do. Understanding these roles is key to troubleshooting and perfecting your recipe.
- Milk Solids (Non-Fat): These are the proteins (casein, whey) and lactose from milk. They provide substance and body to the ice cream, help absorb water, and improve the whipping ability of the mix.
- Fat (from Cream or Butter): Fat is essential for a rich flavor and smooth, creamy texture. During homogenization, fat globules are broken down and coated with proteins, which contributes to a stable structure and slows down melting.
- Sugars (Sucrose, Glucose Syrup): Sugar does more than just add sweetness. It lowers the freezing point of the mix, which ensures the ice cream doesn’t freeze solid like an ice cube. Using a blend of sugars, like sucrose and glucose syrup, can help control both sweetness and ice crystal formation.
- Stabilizers & Emulsifiers: These are the secret heroes.
- Stabilizers (like guar gum, locust bean gum, or carrageenan) absorb free water in the mix, making it thicker and preventing large, crunchy ice crystals from forming during freezing and storage.
- Emulsifiers (like mono- and diglycerides) help the fat and water mix together smoothly, creating a more uniform and stable structure. They are vital for a creamy texture and smooth meltdown.
The Crucial Pre-Treatment Process
Once you have your formula, the mix goes through several critical machine-led steps:
| Process Step | Temperature & Details | Purpose & Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing/Blending | 40-50°C | Ingredients are blended in a heated tank. The warmth helps powders like milk solids and stabilizers dissolve fully without clumping. |
| Pasteurization1 | HTST: 85°C for 15-20 sec | This is a non-negotiable food safety step to eliminate harmful bacteria. High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) pasteurization is efficient and preserves the flavor of the mix better than older, slower methods. |
| Homogenization2 | 65-75°C, 150-200 Bar | The hot mix is forced through a tiny valve at very high pressure. This shatters the large fat globules into tiny ones, resulting in a much smoother, whiter, and more stable mix that resists separation. |
| Aging | 2-4°C for 4-24 hours | The mix is rapidly cooled and held in a refrigerated tank. This "aging" period is vital. It allows the fat to crystallize and the stabilizers to fully hydrate (absorb water), which significantly improves the texture, whipping properties, and melting resistance of the final product. Skipping this step is a common cause of poor quality. |
What is the manufacturing process of making Calippo?
Is manual or semi-automatic filling creating a huge bottleneck in your production? Slow, inconsistent filling not only limits your output but also leads to product waste and higher labor costs. I will explain the fully automated process that transforms your mix into a finished, sealed product ready for market.
The manufacturing process involves pumping the aged mix through a continuous freezer to achieve a soft-serve consistency. Then, a fully automated cup filling and sealing machine dispenses the paper Calippo cups, fills them precisely, applies a foil or paper lid, and heat-seals it shut.
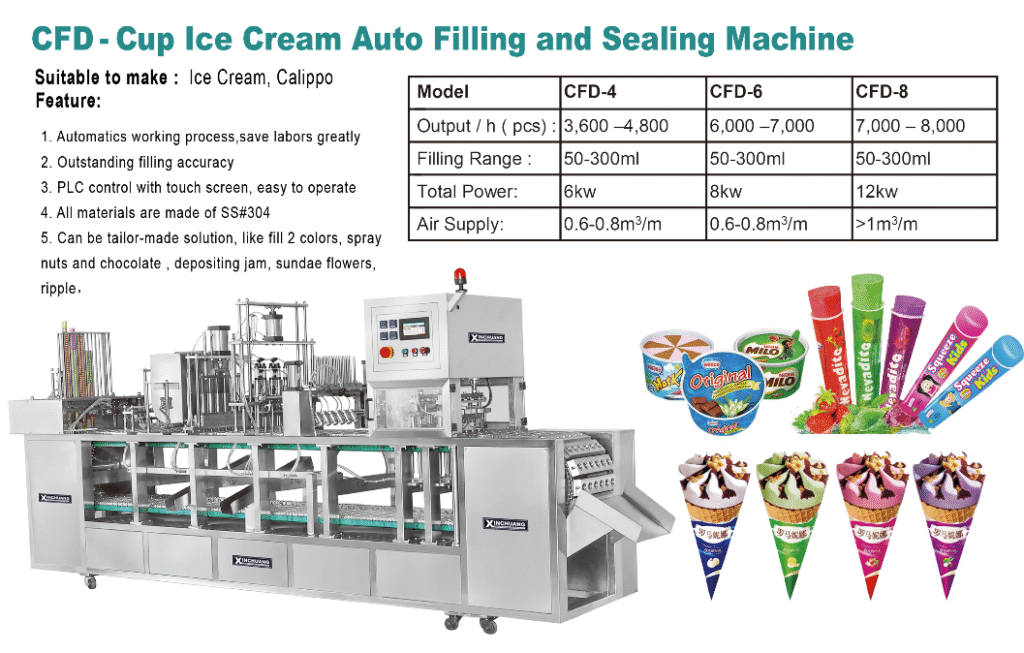
After your ice lolly mix has been perfectly prepared and aged, the real power of modern food manufacturing takes over. This is where specialized machinery, like our Xinchuang cup filling and sealing machines, becomes the heart of your operation. I’ve worked closely with clients from Algeria to Uzbekistan to customize these lines for their specific production goals. The objective is always the same: maximize speed, hygiene, and consistency while minimizing waste.
Stage 1: Continuous Freezing
The aged liquid mix is pumped from the aging tank directly into a continuous freezer. This is not like a home ice cream maker; it’s a high-efficiency scraped-surface heat exchanger3.
- Mechanism: The mix flows into a refrigerated cylinder. Inside, a rotating dasher with sharp scraper blades continuously scrapes the frozen mix off the cylinder walls. This ensures rapid, even freezing and prevents large ice crystals.
- Overrun: As the mix is churned, the freezer injects a controlled amount of air. This is called "overrun4." An overrun of 90% means the final product is nearly 50% air. This air is what makes ice cream light and scoopable, rather than a dense, solid block. The overrun level is a key factor in both texture and product cost.
- Draw Temperature: The ice cream exits the freezer at a "draw temperature" of about -5°C to -8°C. At this temperature, it has the consistency of a very thick, soft-serve ice cream, which is perfect for being pumped and filled into the tubes.
Stage 2: Automated Filling, Sealing, and Hardening
The semi-frozen ice cream is fed directly into the hopper of a rotary filling and sealing machine. This machine is a marvel of automation. I once helped a client in Vietnam double their output by switching from a manual line to one of these.
| Machine Station | Action | Technical Detail & Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Cup Dropping | An empty paper Calippo tube is dropped into a pocket on the rotary table. | Optical sensors ensure that a cup is present before moving to the next station, preventing spills and waste. This is called "no cup, no fill5." |
| Filling | A piston filler nozzle descends into the cup and injects a precise volume of ice cream. | The filler must be volumetric and highly accurate to ensure consistent product weight and control costs. The nozzle often fills from the bottom up to eliminate air pockets. |
| Lid Placing | A mechanical arm with vacuum suction cups picks a single foil lid from a stack and places it on the filled cup. | Precise alignment is critical for a good seal. The vacuum system ensures reliable handling of thin foil lids. |
| Heat Sealing | A heated sealing head presses the lid onto the rim of the cup, melting a thin polymer layer to create an airtight seal. | The temperature, pressure, and dwell time of the sealer must be perfectly calibrated for the specific cup and lid material to ensure product integrity and safety. |
| Ejection & Hardening | The sealed Calippo is ejected onto a conveyor belt that transports it directly into a hardening tunnel or blast freezer. | The product is still soft (-5°C). It must be frozen rapidly to its core temperature of -18°C or lower. This rapid hardening6 keeps ice crystals small, preserving the smooth texture created earlier. |
Conclusion
Producing Calippo-style ice cream requires a two-stage process: first, scientifically preparing a quality mix, and second, using an automated line for freezing, filling, and sealing. Mastering both ensures a top-tier product.
-
Understanding pasteurization is essential for ensuring food safety and quality, making this resource invaluable for anyone in the food industry. ↩
-
Exploring homogenization will reveal its critical role in achieving smooth textures and preventing separation in food products. ↩
-
Understanding this technology can enhance your knowledge of ice cream production and its efficiency. ↩
-
Exploring this concept will help you grasp how air affects ice cream texture and quality. ↩
-
Understanding the ‘no cup, no fill’ system can help you appreciate how automation minimizes waste and enhances efficiency in production. ↩
-
Exploring the significance of rapid hardening will reveal how it preserves texture and quality in ice cream, crucial for manufacturers. ↩

